CAS Numbers:
- Protease: 9001-92-7
- Amylase: 9000-90-2
- Pectate Lyase: 9033-35-6
- Mannanase: 37288-54-3
- Lipase: 9001-62-1
CAS (Chemical Abstracts Service) numbers are unique identifiers assigned to every chemical substance, ensuring accurate identification across the industry.
What are detergent enzymes?
Enzymes in detergent are naturally derived biological catalysts that add extra stain-fighting power to our laundry detergents. Our proprietary blend of different enzymes targets specific types of stains and breaks the soiled mass into smaller molecules that can be easily washed away. These powerful cleaning agents work at the molecular level to tackle tough stains while remaining gentle on fabrics.
What do enzymes in detergent do?
Stains come in many forms and types, including proteins, starches, and lipids. We use several different types of high-quality enzymes to break down a multitude of different stains.
How is our proprietary detergent enzyme blend made?
While the unique proportions and recipe for our enzyme blend are a trade secret, we're happy to share details about the five different types of highly effective cleaning enzymes we use in our laundry detergents.
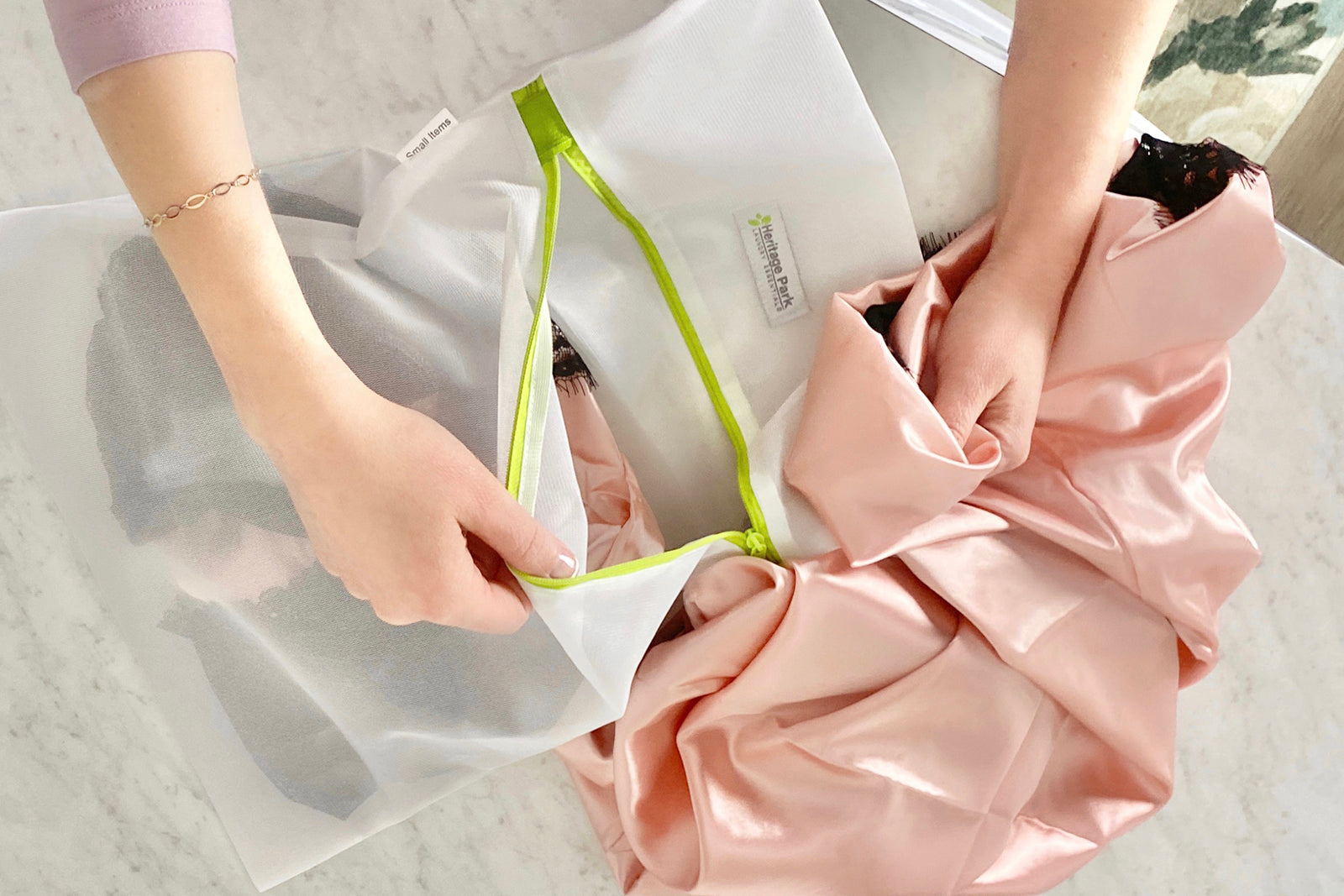
- Protease to target protein. Protein is found in sweat, blood, grass, chocolate, dairy products and milky drinks like tea, coffee and chai. The protease enzyme breaks down the protein molecules in these stains, which makes it easier for the detergent to lift them from the fabric. (Note: many fabrics—including silk, wool, and cashmere—are protein based. This means protease will, over time, degrade the quality of the fabric. For these items, use our enzyme-free Silk & Wool formula.)
- Amylase to target starch. Starch is everywhere! It is commonly used to thicken foods from ready-made sauces and baby foods to dressings and desserts. Unfortunately, starch also acts as a glue for other dirt particles both in the air and in wash water. This makes starch stains super noticeable. Amylase is necessary to break down starch and help wash away these stains.
- Pectate Lyase to target pectin. Pectin is another form of starch that is naturally occurring in our favorite fruits, including berries, bananas and avocados, as well as many vegetables. Pectin can also be added as a thickener to jams, jellies, yogurt drinks and smoothies. It's even used in some cosmetics! Just like starch, pectin can be sticky; pectate lyase is necessary to break down pectin so that the detergent can remove the stain.
- Mannanase to target gum. Guar and locust bean gums can be found in a wide range of foods, including ice cream, mayonnaise and salad dressing. They're also a common ingredient in personal care products like toothpaste and body lotions. Mannanase breaks down these gums to help detergents remove their sticky stains.
- Lipase to target fat, oil and grease. We've all been there: taking a big bite of a delicious cheeseburger only to look down and see a grease stain on our shirt. Ouch. From cheeseburgers to pad Thai, French fries to sausage, pizza to hot dogs, so many of our favorite fast foods leave behind oily stains that are tough to get rid of. Along with the inherent animal fats, many of these items are cooked in oils—peanut, sunflower and sesame. Without the right enzyme, these stains can quickly become permanent. Lipase works to prevent that, by breaking down fats and oils.
The bottom line — if it tastes good, it's almost bound to leave a tricky stain!
How does our laundry detergent enzyme blend work?
We can't spill all our secrets, but we will tell you this—stains can contain more than one component, and will require more than one enzyme to break down. In fact, most everyday stains are multi-layered, with each element in the stain forming a coating. That means an enzyme's access to its target element can be "blocked."
Our enzymes work as a team to clear paths for one another, which boosts their collective power and impact. The result is outstanding performance tackling a wide range of everyday stains, while maintaining color integrity and brightness.
Safety & Certifications
Our proprietary enzyme blend meets the stringent safety standards required for EPA Safer Choice certification:
- EPA Safer Choice Approved: All enzymes pre-approved as safe ingredients meeting EPA's criteria for human health and environmental safety
- Naturally Derived: Enzymes are produced through fermentation processes using microorganisms
- Biodegradable: Enzymes break down naturally in the environment
- Highly Effective: Works at low temperatures and concentrations, reducing energy and water use
- Targeted Action: Each enzyme targets specific stain types, maximizing cleaning efficiency
- Safe for Most Fabrics: Formulated for cotton, polyester, blends, and synthetic materials (Note: NOT suitable for protein-based fabrics like silk, wool, or cashmere—use our enzyme-free Silk & Wool detergents for these materials)
- EWG Verified: Meets Environmental Working Group's strictest standards for health and transparency
All Heritage Park detergents containing this ingredient are both EPA Safer Choice Certified and EWG VERIFIED®, providing independent, third-party validation of safety.
What product is this ingredient in?
All-Purpose Detergents:
- Heritage Park All-Purpose Laundry Detergent - Fragrance-Free
- Heritage Park All-Purpose Laundry Detergent - Shore Breeze
- Heritage Park All-Purpose Laundry Detergent - Lavender Mist
- Heritage Park All-Purpose Laundry Detergent - Spring Magnolia
Specialty Detergents:
Important Note: Our Silk & Wool detergents are enzyme-free to protect protein-based fibers.